1931, kistler inventedaerogel, after more than 90 years of publication, the excellent physical and chemical properties of aerogels have broken 15 Guinness World Records.
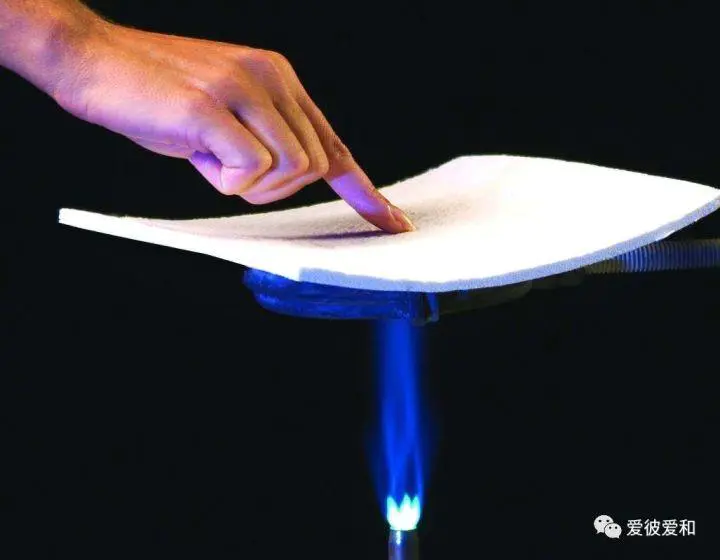
1, the lowest thermal conductivity
aerogels inhibit the contribution of gas molecules to heat conduction, and the thermal conductivity can be lower than 0.016W/(m · K). By means of doping, the radiation heat conduction of silicon aerogel can be further reduced, and the thermal conductivity of carbon-doped aerogel can be as low as 0.013W/(m-K) at normal temperature and pressure, which is the solid material with the lowest thermal conductivity at present.

2, minimum density
aerogel has long been in the Guinness Book of World Records as the lightest solid material. In recent years, this record has been constantly refreshed. In 2015, the nanofiber research team led by academician Yu Jianyong and professor ding bin of Donghua university developed an ultra-light and ultra-elastic fiber aerogel using common fiber membrane materials. the results of China's metrology certification show that the solid material density of this fiber aerogel is only 0.12 mg/cm3, which is about 1/10 of the air density.

3, the widest density range
, because of the different tissue components and different manufacturing processes, the density of aerogels varies widely-the bulk density is adjustable in the range of 0.0012-0.500g/m3. This gives aerogel materials a broader application space.
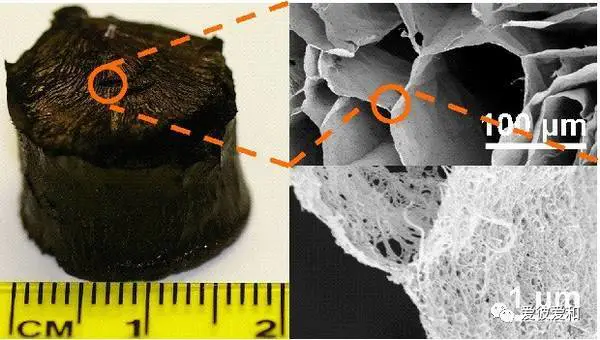
4, the widest compression modulus
aerogels can vary over a range of 6 orders of magnitude. Such a wide range of compression modulus determines the density adjustability of the aerogel material, so that functional applications with different density requirements can be realized.
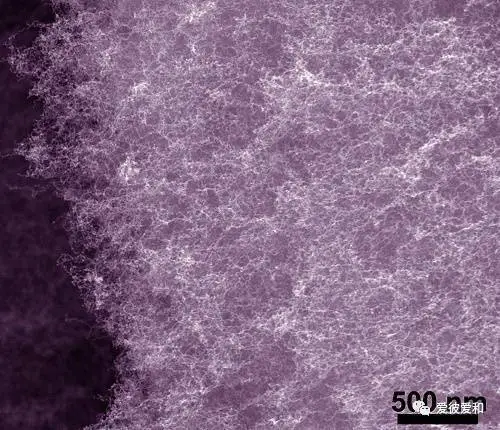

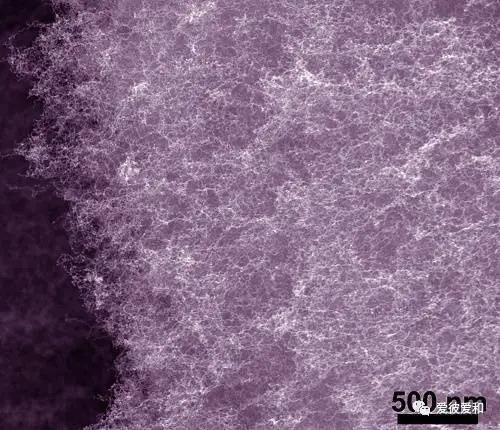
5, the smallest aperture
aerogel is generally around 50nm, and the smallest pore size can even be less than 1nm. The fine nano-scale structure makes the thermal conductivity of the aerogel material extremely low and has a great specific surface area.
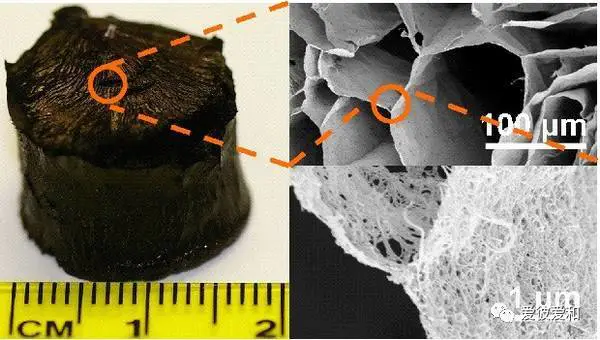
6, the highest hole rate
aerogel can be as high as 99.9 percent, and the numerous small pores on the surface make it an ideal material for adsorbing pollutants in water. Moreover, it has a particularly large ratio product. Aerogels also have broad application prospects as new catalysts or catalyst carriers.

7, the lowest speed of sound propagation
the porous network structure of aerogels makes them have ultra-low density, so that the propagation speed of sound waves in aerogels is much slower than that of general solid materials. The propagation velocity of acoustic waves within the aerogel may be as low as 70 m/s.
8, the highest acoustic impedance
aerogel is as high as 106kg/m2 · s, the longitudinal acoustic propagation velocity of aerogel is very low, and the acoustic resistance varies with the density in a large range, so it is an ideal acoustic impedance coupling material.
9, the lowest dielectric constant
aerogel material is less than 1.003, which is a good dielectric material, which can reduce the leakage current of the integrated circuit, reduce the capacitance effect between the wires, and reduce the heating of the integrated circuit.
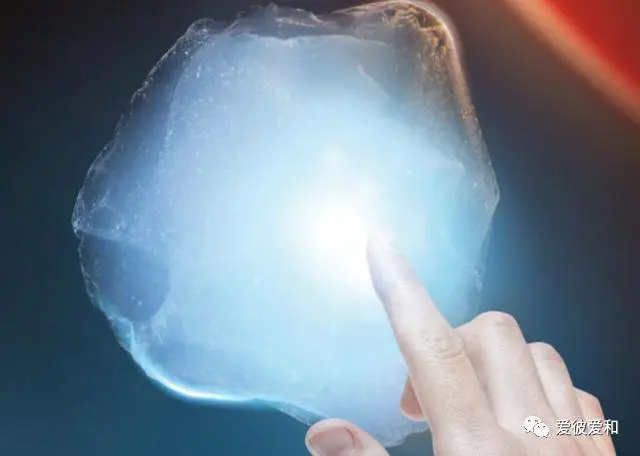
10, the lowest refractive index
, because of the extremely high proportion of air in the aerogel, it has a very low refractive index-up to 1.0003, very close to the refractive index of air (1.0). This property has been used by scientists in optical materials.

11, the widest refractive index range
aerogel is very good. By regulating the density of aerogel, the refractive index can be continuously adjusted between 1.0003-1.24, which can be used to make detectors.
12, the lowest loss angle tangent.
aerogel has a very low loss tangent, and its loss tangent value is less than 10-4, so its wave transmission is very good and it is a good wave-transmitting material.

13, the lowest Young's modulus
aerogel is less than 106N/m2, 4 orders of magnitude lower than the corresponding non-porous glassy materials.
14, the first sample returned from a comet
the first time humans collected samples from a comet, they used aerogel gloves ". This precious material returned to Earth on January 15, 2006. The sample came from Comet 2. Currently, scientists are analyzing and understanding the chemical composition of this primitive ice body.

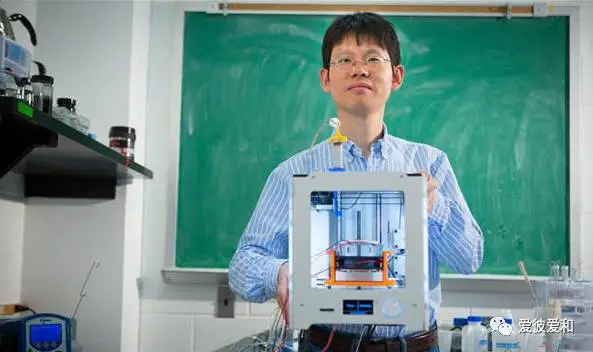
15, the smallest density of 3D printing structure
3D printed graphene aerogels developed in February 2016 by researchers from Kansas State University and the University of Buffalo, State University of New York (both in the United States) and Harbin Institute of Technology (China), materials engineers from different universities, have been rated by Guinness World Records as the "least dense 3D printed structure" with a density of only 0.5 mg/cm.3.